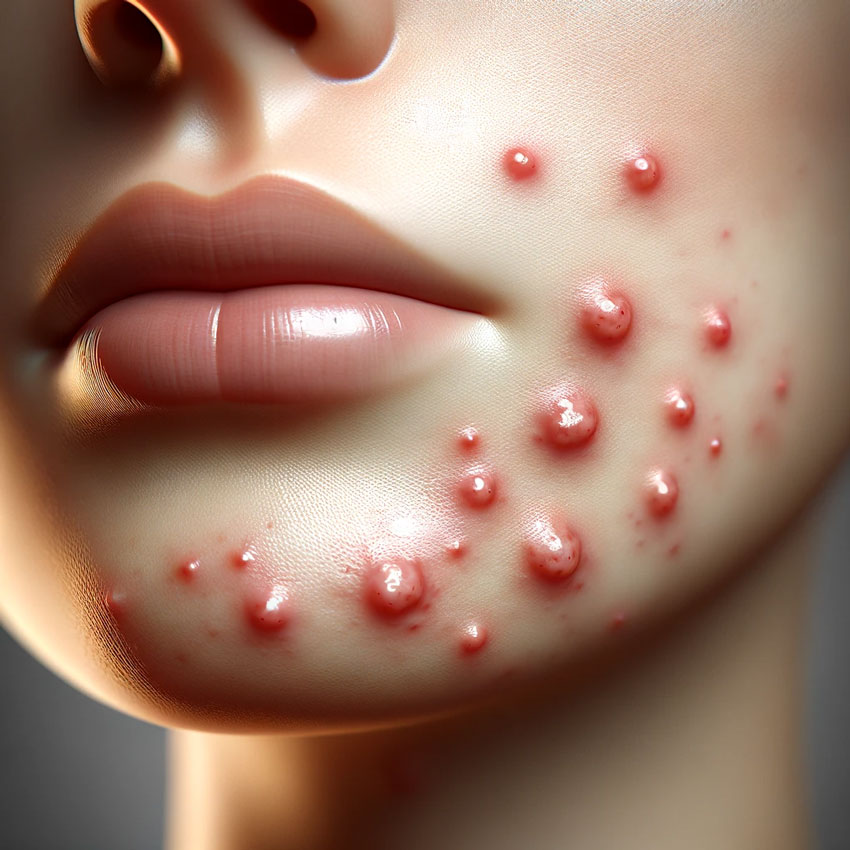
Cystic acne, often described as the most severe form of acne, presents a significant challenge for millions worldwide.
This article delves into the underlying causes of this skin condition, characterized by deep, painful cysts and nodules that can lead to significant scarring.
Beyond a mere surface issue, cystic acne is a complex interplay of hormonal imbalances, genetics, and environmental factors.
We will explore the latest dermatological advancements and holistic approaches to treating cystic acne, offering hope and practical solutions for those battling this persistent skin condition.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower readers with knowledge and strategies to effectively manage and overcome the challenges of cystic acne, restoring not only skin health but also self-confidence.
Understanding Cystic Acne
Cystic acne is a severe form of acne that affects the skin. It is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause painful, pus-filled cysts to form deep under the skin.
The condition is caused by a combination of factors, including excess oil production, bacteria, and inflammation.
Cystic acne is characterized by the formation of large, red, painful breakouts deep in the skin. These breakouts can occur anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the face, chest, and shoulders.
The cysts associated with cystic acne are filled with pus and can be quite large. They can be painful to the touch and can take a long time to heal.
Cystic acne is caused by a combination of factors, including excess oil production, bacteria, and inflammation.
The excess oil production can cause the pores in the skin to become clogged, leading to the formation of cysts. Bacteria can also get trapped in the pores, leading to inflammation and the formation of cysts.
Cystic acne can be a difficult condition to treat. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of cystic acne. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment options for cystic acne can include topical medications, oral medications, and in some cases, surgical procedures.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cystic acne is caused by a combination of factors, including hormones, genetics, and bacteria.
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, or menstrual cycles, can cause an increase in sebum production, which can lead to clogged pores.
Genetics also play a role, as individuals with a family history of acne are more likely to develop cystic acne.
Diet may also play a role in the development of cystic acne, as consuming foods high in sugar and carbohydrates can cause an increase in insulin production, which can lead to an increase in sebum production.
Stress can also contribute to the development of cystic acne, as it can cause an increase in the production of hormones that can lead to an increase in sebum production.
Cystic acne occurs when bacteria gets trapped in clogged pores, causing inflammation and swelling. Excess oil production and dead skin cells can also contribute to the development of cystic acne. Hair follicles can also become clogged, leading to the formation of cystic acne.
Symptoms and Complications
Cystic acne is a severe form of acne that causes painful, red, and inflamed nodules to form deep under the skin. These nodules can be as large as 5mm in diameter and are often filled with pus. Cystic lesions can occur anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the face, neck, chest, and back.
One of the most significant complications of cystic acne is scarring. Because the nodules are so deep under the skin, they can cause significant damage to the surrounding tissue. This can lead to the formation of acne scars, which can be difficult to treat and may last a lifetime.
In addition to physical symptoms, cystic acne can also cause emotional distress. The appearance of cystic acne can be embarrassing and may lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
It is essential to seek treatment for cystic acne as soon as possible to prevent these complications.
Some of the most common symptoms of cystic acne include:
- Painful, red, and inflamed nodules
- Cystic lesions that are filled with pus
- Scarring
- Emotional distress
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek treatment from a dermatologist or other healthcare provider. They can provide you with a personalized treatment plan to help manage your symptoms and prevent complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Cystic acne is a severe form of acne that requires medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. A dermatologist or doctor can diagnose cystic acne by examining the skin and reviewing the patient’s medical history.
Treatment for cystic acne can vary depending on the severity of the condition.
Mild cases may be treated with over-the-counter topical medications containing benzoyl peroxide, adapalene, or tretinoin. These medications work by reducing inflammation and unclogging pores.
For more severe cases of cystic acne, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
Isotretinoin, also known as Accutane, is a powerful medication that is reserved for the most severe cases of cystic acne. It is a retinoid medication that reduces oil production and prevents the formation of new cysts.
In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend steroid injections to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Corticosteroids are injected directly into the cyst to reduce inflammation and pain.
It is important to note that treatment for cystic acne can take several months to show significant improvement, and it may take even longer for the skin to fully heal.
Patients should follow their dermatologist’s or doctor’s instructions carefully and be patient with the treatment process.
Prevention and Home Remedies
Preventing cystic acne is not always possible, but there are steps a person can take to reduce the likelihood of developing it.
One of the most important things a person can do to prevent cystic acne is to keep their skin clean. A gentle cleanser can help remove excess oil and dirt from the skin, which can reduce the risk of developing acne.
It is important to avoid harsh cleansers or exfoliants, as they can irritate the skin and make acne worse.
Moisturizing the skin is also important. Using a non-comedogenic lotion or cream can help keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
It is important to avoid oily or greasy products, as they can contribute to acne breakouts.
Wearing loose-fitting clothing and avoiding tight clothing can also help prevent acne. Tight clothing can trap sweat and oil against the skin, which can contribute to acne breakouts.
There are also several home remedies that may help reduce the symptoms of cystic acne.
Ice can be applied to the affected area to reduce inflammation and swelling. Aspirin masks can be made by crushing aspirin tablets and mixing them with water to form a paste. This can be applied to the skin to reduce inflammation and redness.
Diet can also play a role in preventing cystic acne. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help keep the skin healthy and reduce the risk of developing acne.
It is important to avoid foods that are high in sugar or processed foods, as these can contribute to acne breakouts.
Impact on Life and Coping Strategies
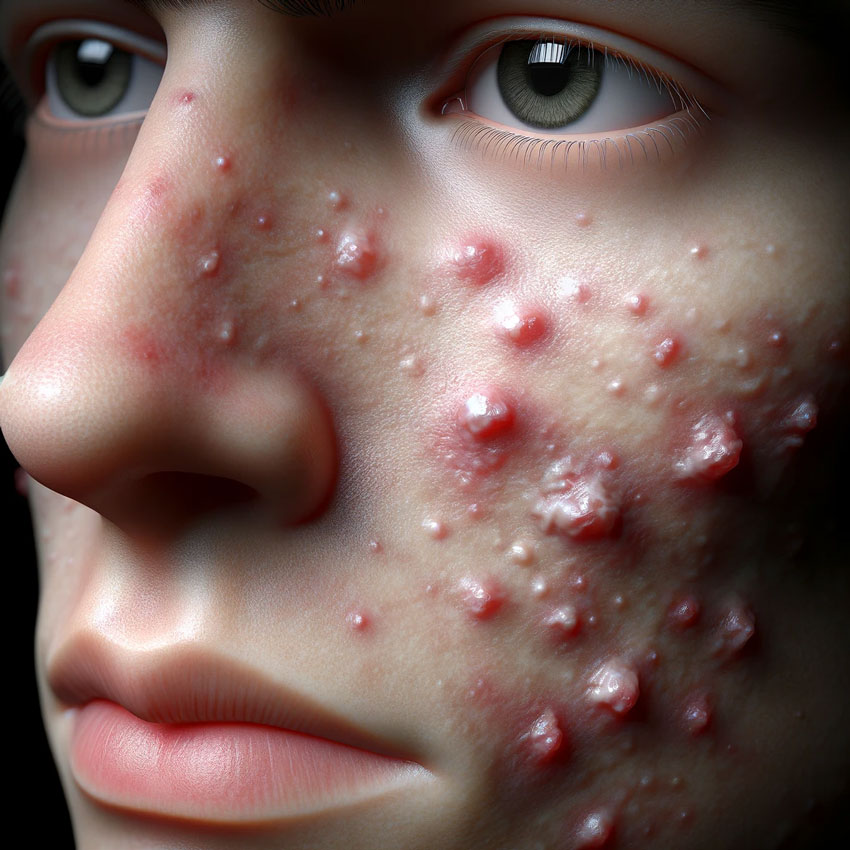
Cystic acne can have a significant impact on a person’s life, affecting their self-esteem, confidence, and social interactions. It can also lead to emotional distress, especially in teenagers, who may already be struggling with body image issues.
For women, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or while taking birth control or oral contraceptives can exacerbate cystic acne. This can make it even more challenging to manage and cope with the condition.
Fortunately, there are several coping strategies that can help individuals manage the emotional impact of cystic acne. These include:
- Acknowledging and accepting their feelings: It’s essential to recognize and accept the emotions that come with cystic acne, such as frustration, anxiety, and depression. This can help individuals better manage their emotional responses and develop effective coping strategies.
- Seeking support: Talking to friends, family members, or a mental health professional can provide much-needed support and help individuals work through their emotions.
- Practicing self-care: Engaging in activities that promote self-care, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies, can help individuals feel more confident and improve their overall well-being.
- Focusing on strengths: It’s important to focus on personal strengths and accomplishments, rather than solely on physical appearance. This can help individuals build self-esteem and feel more positive about themselves.